Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Risk of Diabetes in Patients with Long-Standing Graves’ Disease: A Longitudinal Study
- Eyun Song, Min Ji Koo, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Jung A Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1277-1286. Published online December 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1251
- 5,181 View
- 181 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The detrimental effects of excessive thyroid hormone on glucose metabolism have been widely investigated. However, the risk of diabetes in patients with long-standing hyperthyroidism, especially according to treatment modality, remains uncertain, with few longitudinal studies.
Methods
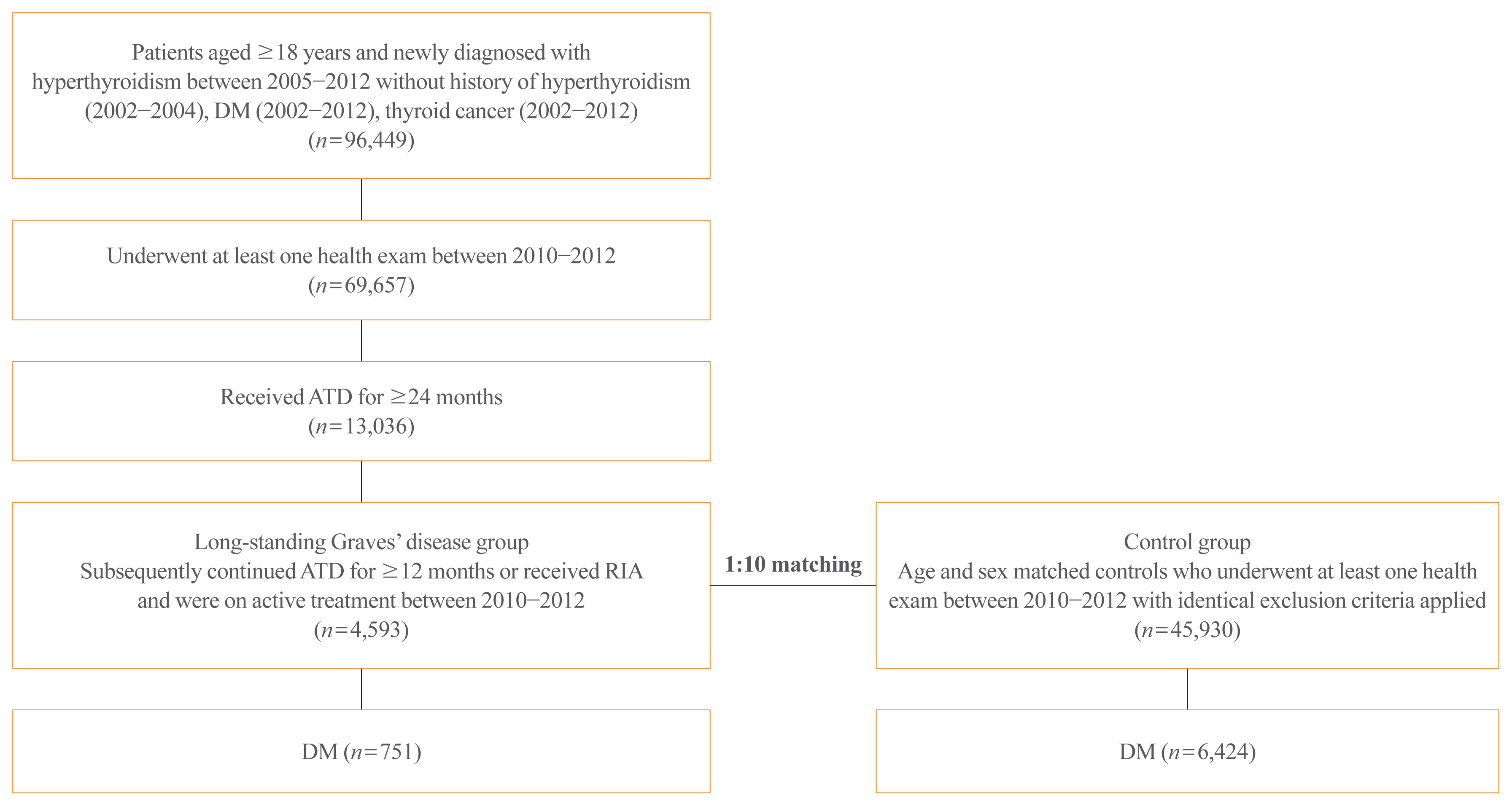
The risk of diabetes in patients with Graves’ disease treated with antithyroid drugs (ATDs) for longer than the conventional duration (≥2 years) was compared with that in age-and sex-matched controls. The risk was further compared according to subsequent treatment modalities after a 24-month course of ATD: continuation of ATD (ATD group) vs. radioactive iodine ablation (RIA) group.
Results
A total of 4,593 patients were included. Diabetes was diagnosed in 751 (16.3%) patients over a follow-up of 7.3 years. The hazard ratio (HR) for diabetes, after adjusting for various known risk factors, was 1.18 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 1.28) in patients with hyperthyroidism. Among the treatment modality groups, the RIA group (n=102) had a higher risk of diabetes than the ATD group (n=4,491) with HR of 1.56 (95% CI, 1.01 to 2.42). Further, the risk of diabetes increased with an increase in the ATD treatment duration (P for trend=0.019).
Conclusion
The risk of diabetes was significantly higher in patients with long-standing Graves’ disease than in the general population, especially in patients who underwent RIA and prolonged ATD treatment. Special attention to hyperglycemia during follow-up along with effective control of hyperthyroidism may be necessary to reduce the risk of diabetes in these patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety of non-standard regimen of systemic steroid therapy in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy: a single-centre experience
Nadia Sawicka-Gutaj, Dawid Gruszczyński, Natalia Zawalna, Kacper Nijakowski, Agnieszka Skiba, Mateusz Pochylski, Jerzy Sowiński, Marek Ruchała
Pharmacological Reports.2024; 76(1): 185. CrossRef - Increased risk of diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Hwa Young Ahn, Jooyoung Lee, Jinmo Kang, Eun Kyung Lee
European Journal of Endocrinology.2024; 190(3): 248. CrossRef - Prevalencia de diabetes en personas con disfunción tiroidea
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Medicina Clínica.2023; 160(8): 333. CrossRef - Control of Thyroid Dysfunction in Spanish Population Registered in
the Primary Care Clinical Database: An Analysis of the Proportion of Patients
with Thyrotropin Values Outside the Reference Range
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(03): 184. CrossRef - Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction and its relationship to income level and employment status: a nationwide population-based study in Spain
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Hormones.2023; 22(2): 243. CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetes in people with thyroid dysfunction
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Medicina Clínica (English Edition).2023; 160(8): 333. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Endocrine Diseases: An Update of Diagnostic and Treatment Particularities
Mihaela Simona Popoviciu, Lorena Paduraru, Raluca Marinela Nutas, Alexandra Maria Ujoc, Galal Yahya, Kamel Metwally, Simona Cavalu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(16): 12676. CrossRef - Thyroid Eye Disease and Its Association With Diabetes Mellitus: A Major Review
Roshmi Gupta, Pramila Kalra, Lakshmi B. Ramamurthy, Suryasnata Rath
Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery.2023; 39(6S): S51. CrossRef - Metabolite Changes during the Transition from Hyperthyroidism to Euthyroidism in Patients with Graves’ Disease
Ho Yeop Lee, Byeong Chang Sim, Ha Thi Nga, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Nguyen Thi Linh, Sang Hyeon Ju, Dong Wook Choi, Daiki Setoyama, Hyon-Seung Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 891. CrossRef - Diabetes and Hyperthyroidism: Is There a Causal Link?
Sang Yong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1175. CrossRef
- Safety of non-standard regimen of systemic steroid therapy in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy: a single-centre experience


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



